Read: Multiply and Divide Complex Numbers
Learning Objectives
- Multiply complex numbers.
- Find conjugates of complex numbers.
- Divide complex numbers.
- Simplify powers of i
Multiplying complex numbers is much like multiplying binomials. The major difference is that we work with the real and imaginary parts separately.
Multiplying a Complex Number by a Real Number
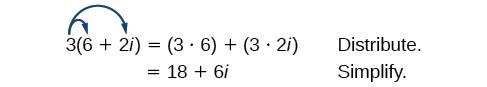 Let’s begin by multiplying a complex number by a real number. We distribute the real number just as we would with a binomial. So,for 3(6+2i), 3 is multiplied to both the real and imaginary parts. So we have [latex](3)(6)+(3)(2i)[/latex] = [latex]18 + 6i[/latex].
Let’s begin by multiplying a complex number by a real number. We distribute the real number just as we would with a binomial. So,for 3(6+2i), 3 is multiplied to both the real and imaginary parts. So we have [latex](3)(6)+(3)(2i)[/latex] = [latex]18 + 6i[/latex].
How To: Given a complex number and a real number, multiply to find the product.
- Use the distributive property.
- Simplify.
- Put answer in a+bi form.
Example
Find the product [latex]4\left(2+5i\right)[/latex].Answer:
Distribute the [latex]4[/latex].
Multiplying Complex Numbers Together
Now, let’s multiply two complex numbers. We can use either the distributive property or the FOIL method. Recall that FOIL is an acronym for multiplying First, Outer, Inner, and Last terms together. Using either the distributive property or the FOIL method, we get
Because [latex]{i}^{2}=-1[/latex], we have
To simplify, we combine the real parts, and we combine the imaginary parts.
How To: Given two complex numbers, multiply to find the product.
- Use the distributive property or the FOIL method.
- Simplify.
- Put answer in a+bi form.
Example
Multiply [latex]\left(4+3i\right)\left(2 - 5i\right)[/latex].Answer:
Use [latex]\left(a+bi\right)\left(c+di\right)=\left(ac-bd\right)+\left(ad+bc\right)i[/latex]
Simplifying Powers of i
The powers of i are cyclic. Let’s look at what happens when we raise i to increasing powers.
We can see that when we get to the fifth power of i, it is equal to the first power. As we continue to multiply i by itself for increasing powers, we will see a cycle of [latex]4[/latex]. Let’s examine the next [latex]4[/latex] powers of i.
Example
Evaluate [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex].Answer:
Since [latex]{i}^{4}=1[/latex], we can simplify the problem by factoring out as many factors of [latex]{i}^{4}[/latex] as possible. To do so, first determine how many times [latex]4[/latex] goes into [latex]35[/latex]: [latex]35=4\cdot 8+3[/latex].
Q & A
Can we write [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] in other helpful ways?
As we saw in Example 11, we reduced [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] to [latex]{i}^{3}[/latex] by dividing the exponent by 4 and using the remainder to find the simplified form. But perhaps another factorization of [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] may be more useful. The table below shows some other possible factorizations.
| Factorization of [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{34}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{33}\cdot {i}^{2}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}\cdot {i}^{4}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}\cdot {i}^{16}[/latex] |
| Reduced form | [latex]{\left({i}^{2}\right)}^{17}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{33}\cdot \left(-1\right)[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}\cdot 1[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}\cdot {\left({i}^{4}\right)}^{4}[/latex] |
| Simplified form | [latex]{\left(-1\right)}^{17}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]-{i}^{33}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}[/latex] |
Each of these will eventually result in the answer we obtained above but may require several more steps than our earlier method.
Dividing Complex Numbers
Division of two complex numbers is more complicated than addition, subtraction, and multiplication because we cannot divide by an imaginary number, meaning that any fraction must have a real-number denominator. This idea is similar to rationalizing the denominator of a fraction that contains a radical. To eliminate the complex or imaginary number in the denominator, you multiply by the complex conjugate of the denominator, which is found by changing the sign of the imaginary part of the complex number. In other words, the complex conjugate of [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex].
Note that complex conjugates have a reciprocal relationship: The complex conjugate of [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex], and the complex conjugate of [latex]a-bi[/latex] is [latex]a+bi[/latex]. Further, when a quadratic equation with real coefficients has complex solutions, the solutions are always complex conjugates of one another.
Suppose we want to divide [latex]c+di[/latex] by [latex]a+bi[/latex], where neither a nor b equals zero. We first write the division as a fraction, then find the complex conjugate of the denominator, and multiply.
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
Apply the distributive property.
Simplify, remembering that [latex]{i}^{2}=-1[/latex].
A General Note: The Complex Conjugate
The complex conjugate of a complex number [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex]. It is found by changing the sign of the imaginary part of the complex number. The real part of the number is left unchanged.
- When a complex number is multiplied by its complex conjugate, the result is a real number.
- When a complex number is added to its complex conjugate, the result is a real number.
Example
Find the complex conjugate of each number.
- [latex]2+i\sqrt{5}[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{1}{2}i[/latex]
Answer:
- The number is already in the form [latex]a+bi[/latex]. The complex conjugate is [latex]a-bi[/latex], or [latex]2-i\sqrt{5}[/latex].
- We can rewrite this number in the form [latex]a+bi[/latex] as [latex]0-\frac{1}{2}i[/latex]. The complex conjugate is [latex]a-bi[/latex], or [latex]0+\frac{1}{2}i[/latex]. This can be written simply as [latex]\frac{1}{2}i[/latex].
Analysis of the Solution
How To: Given two complex numbers, divide one by the other.
- Write the division problem as a fraction.
- Determine the complex conjugate of the denominator.
- Multiply the numerator and denominator of the fraction by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
- Simplify.
- Put answer in a+bi form.
Example
Divide [latex]\left(2+5i\right)[/latex] by [latex]\left(4-i\right)[/latex].Answer:
We begin by writing the problem as a fraction.
Then we multiply the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
To multiply two complex numbers, we expand the product as we would with polynomials (the process commonly called FOIL).
[latex]\begin{array}{rcll}\Large{\frac{(2+5i)}{(4-i)}}\cdot\frac{(4+i)}{(4+i)}&=&\Large{\frac{8+2i+20i+5{i}^{2}}{16+4i - 4i-{i}^{2}}}& \\&=&\Large{\frac{8+2i+20i+5(-1)}{16+4i - 4i-(-1)}}&\quad\text{Because }i^2=-1\\&=&\Large{\frac{3+22i}{17}}& \\&=&\Large{\frac{3}{17}+\frac{22}{17}i}&\quad\text{Separate real and imaginary parts}\end{array}[/latex]
Note that this expresses the quotient in standard form.
Summary
Multiplying complex numbers is similar to multiplying polynomials. Remember that an imaginary number times another imaginary numbers gives a real result. When you divide complex numbers you must first multiply by the complex conjugate to eliminate any imaginary parts, then you can divide.Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Ex: Raising the imaginary unit i to powers. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Dividing Complex Numbers. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at: http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface.

Although we have seen that we can find the complex conjugate of an imaginary number, in practice we generally find the complex conjugates of only complex numbers with both a real and an imaginary component. To obtain a real number from an imaginary number, we can simply multiply by [latex]i[/latex].
In the last video you will see more examples of dividing complex numbers. https://youtu.be/XBJjbJAwM1c