Introduction to Polynomial Basics
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this section, you will be able to:- Identify the degree, leading coefficient, and leading term of a polynomial.
- Add and subtract polynomials.
- Multiply polynomials.
- Square a binomial.
- Find a difference of squares.
- Perform operations on polynomials with several variables.
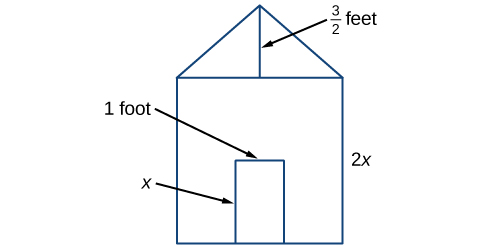 Figure 1
Figure 1[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill A& =& {s}^{2}\hfill \\ & =& {\left(2x\right)}^{2}\hfill \\ & =& 4{x}^{2}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Then, find the area of the triangle in square feet.
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill A& =& \frac{1}{2}bh\hfill \\ & =& \text{}\frac{1}{2}\left(2x\right)\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)\hfill \\ & =& \text{}\frac{3}{2}x\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Next, find the area of the rectangular door in square feet.
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill A& =& lw\hfill \\ & =& x\cdot 1\hfill \\ \hfill & =& x\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
[latex]4{x}^{2}+\frac{3}{2}x-x[/latex] ft2, or [latex]4{x}^{2}+\frac{1}{2}x[/latex] ft2.
In this module, we will examine expressions such as this one which combine several variable terms.Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution.
